Fore words
As we were coming down towards the end of the Academic year, I promised to give you a guideline on how to go about writing your proposal. Kindly take time to read the guideline and try to see how you can accommodate these procedures when writing your proposal.
Take this guideline as benchmark for writing your proposal. Therefore you need to consult as many research books as possible so as to enrich the contents of this guideline and come up with a proposal of recommendable standard.
However, these guidelines differ much depending on the nature of the University and Discipline. Therefore, there is no common format/approach for writing proposals across Universities and Disciplines.
As you write your proposal make note of the following:
(i) You are undergraduate student; therefore, your work must reflect that you are a mature academician ready for an independent work.
(ii) Try to adhere to all principles of academic writing, remember plagiarism is a crime against scholarship. Therefore your arguments must be supported by proper citations/acknowledgement of sources.
(iii) Take time to read extensively and intensively about your research topic so that you are aware and sure of what you intend to do. This will help you in defining your problem, stating your objectives, stating your problem, identifying knowledge gap, and deciding on appropriate research methods to adopt.
Chapter One
The problem and its setting.
1.0 Introduction
This section aims at introducing a chapter. It highlights major parts of the first chapter. At this point therefore, you need to point out/outline all the major parts of the first chapter. This section must be short paragraph (not more than five sentences) offering a summary of the contents of the chapter.
For example: this chapter is presented under the following sections: background information; statement of the problem; and objectives of the study. Other sections are research questions/hypothesis (depending on your choice); significance of the study and definition of key terms and concepts. Delimitation of the study is also included in this chapter.
1.1.0 Background to the problem
This section is the heart of the research. It should be at lest 2 pages long. The section forms the basis of other sections of your research. For example: justification of the study, objectives of the study, statement of the problem, and knowledge gap. Therefore, this section should be written in a very precise manner to give a complete picture of your work. A well defined background will produce good objectives, good statement of the problem and will clearly show what is known about the study and what is not known. Give all the information that will help your examiner to understand the generality of the problem. You just need to briefly explain how a particular problem has arisen and why is it a problem. It should be noted that, background information is a summary of your literature review.
Generally what is expected at this point is:
- Give a brief history of the problem, stating clearly why the problem exists with reference to various scholars.
- What is known about the study, give the major arguments raised by various scholars
- State what is not known (indicate why you believe that it is, in fact, a researchable problem).
1.2.0 Statement of the problem
This is a summary of the background section. This section should not go beyond one paragraph. A candidate needs to state what is known about the study, what is not known about the study and what is expected out of the study.
For example: Existing literatures about the causes of truancy indicates that…………………………………..Astounding as it may appear, there is no major study on the role of parents towards high rate of truancy in Tanzanian primary schools, particularly in Nyamagana District. Therefore, this study seeks to find out and establish the role of parents towards high rate of truancy in Nyamagana District.
1.3.0 Objectives of the study
These states what the researcher seeks to achieve at the completion of the research project. This is important because it is the basis for evaluating whether the research has accomplished what it set out to do.
1.3.1 Main objective
This refers to the general intention of the research. It should spell what the research is supposed to accomplish. In most cases it carries the title of the study.
1.3.2 Specific objectives
These are specific objectives arising directly from the general objective of the study. These are normally stated in measurable terms such as
- To identify……..
- To determine……..
- To describe……….
- To establish……….
- To find out……….
1.3.3 Research questions
These are specific objectives translated into questions. They are investigative assumptions, which guide the study. Each specific objective is translated into an independent question, therefore, the number of specific objectives determine the number of research questions to e developed.
1.4.0 Significance of the study
This refers to the relevance of the study in terms of academic contributions and practical use that might be made of the findings. It should reflect on knowledge creation or socio-economic value to the community.
Therefore, you need to identify the key beneficiaries (field of study, researchers, academicians, community or other stake holders in the area of study) of your study and describe how each beneficiary is going to benefit. In other words what will be the contribution of the new knowledge that you are going to generated?
For example:
(The title of the study was: The Role of Peasants in Struggles for Independence of Tanagnyika)
Findings from the study will push forward historical investigations of struggles for independence in new directions, showing the ways in which grassroots activists, particularly peasants were critical in struggles for independence in Tanganyika. Therefore, results would lay the basis for understanding the role of peasants in struggles for independence elsewhere in Africa, and third world in general where peasants were and are dominant. Also the study provides significant insights, which will be helpful to teachers, students, politicians, historians and other interested researchers in the study of political history particularly in Sukuma land and Tanzania in general
1.5.0 Delimitation of the study
At this point a candidate needs to define geographical and academic limits of the study. For example:
The study will be conducted in ………..District from four wards. Teachers, Ward Educational officers, Head of schools, parents and students will be involved. The study will deal with the role of parents only towards high rate truancy in Nyamagana District.
1.6.0 Definition of key terms and concepts
The same words may have different connotations to people, especially if they work in various disciplines. List and clarify or define the main words and concepts that you will use in your research.
Chapter two
Literature review.
1.0 Introduction:
This part aims at introducing the chapter.
For example: this section is about literature review related to the study. It is divided into two parts, Empirical Literature and Synthesis and research gap.
- Empirical literature:
An adequate literature review is required in all research proposals. The purpose of literature review is:
- To provide evidence to the examiner that a candidate is well acquainted with past and current knowledge in the field of study. This will help to identify the known and unknown knowledge
- To prove that the research will not duplicate past or current knowledge
- Literature review positions your research within the existing body of knowledge.The gathered evidence should be from different parts of the world and specifically from at least each continent.
- Research gap
This is the gap in knowledge that a researcher wants to fill through his/her research. It is established after a thorough review of literatures. Literature review helps a researcher to know about the existing knowledge and missing knowledge (research gap).

Source
Chapter three
Research methodology
1.0 Introduction
This part usually introduces the chapter. It outlines the major components of the third chapter. For example:
This Chapter presents Research Methodology through which information relevant to the research problem will be collected. In this area of Research methodology, the Researcher stated various steps and techniques that will be used in studying the research problem. The Chapter is presented under the following sections; Research design, Area of study and Sample and Sample size. Other sections are Data collection methods and Reliability and Validity of instruments.
3.1.0 Research design
At this point a candidate is expected to define the term research design, identify the kind of research design he/she will employ in his /her study (qualitative or quantitative design), give reason(s) for selecting a particular design (why qualitative or quantitative design) and state how a selected design will be used in the field.
3.2.0 Study area
At this point a candidate is expected to give a thorough description of the study area. The most important information for this section is outlined below:
- Geographical information, including climatic information (temperature, rainfall, vegetation, soil, drainage) and geographical position (latitudes and longitudes) of the area are important.
- Administrative information of the region, including administrative boundaries. It is important to include the following maps: Map of your country, map of the region and district
- Social information like the people inhabiting the area, language(s) spoken, and culture of the people.
- Economic information, particularly economic activities taking place in the region and economic status of the region are important
- Demographic information (population data of the area)
- Justification of the study area. Why is it important for the study to be conducted in the proposed area? It is important to have credible evidence from sources.
3.3.0 Sample and sample size
A candidate is expected to:
- Define a term sample
- Give the expected sample size (e.g. 100 respondents)
- Give reasons for selecting such a sample size ( e.g. due to limitation of resources, time and geographical accessibility)
- Describe the numerical composition of your sample (e.g. in particular the sample will consists of 30 teachers, 20 head of schools, 25 parents 25 students)
3.4.0 Sampling procedures
These guarantees that the data is representative and a basis for generalizing the conclusion.
A candidate is expected to
- Define the term sampling procedures
- Identify the sampling procedures he/she will employ in the study
- Describe each selected procedure
- Give reasons for selecting each procedure
- Describe the way he/she will use each sampling procedure in getting respondents (e.g. x sampling procedure will be used in sampling A&B respondents because…………)
3.5.0 Data collection methods
A candidate is expected to
- Define the term data collection methods
- State why is it important to use a variety of data collection methods in research
- Identify the kind of data collection method he/she will use in the field (e.g. this study will employ the following methods of data collection; interview, questionnaires, documentary review (must be employed) and Focus Group Discussion. Then describe the identified methods as follows:
3.5.1 Interview
- Define the term interview
- Give reasons for choosing this method
- State to whom(what kind of respondents) the method will be administered
- Explain how you will use/administer this method in the field
3.5.2 Questionnaire
- Define the term questionnaire
- Describe the kind of questionnaires you will use in the field ( Close or Open ended)
- Give reasons for choosing this method
- State to whom(what kind of respondents) the method will be administered
- Explain how you will use/administer this method in the field
3.5.3 Documentary review
- Define the term documentary review
- Outline the kind of documents that you think are important in your study
- Explain where you will get such documents
- Give reasons as to why documentary review is important in your study
3.6.0 Validity and Reliability
3.6.1 Reliability
- Define the term reliability
- Give reasons why reliability is it important to consider reliability when preparing a proposal (research instruments)
- Explain how you would ensure reliability of your research instrument
3.6.2 Validity
- Define the term validity
- Explain why is it important to validate research instruments?
- Explain how you would ensure validity of your research instruments?
3.7.0 Data analysis plan
A candidate is expected to give a plan on how she/he will analyze the data collected.
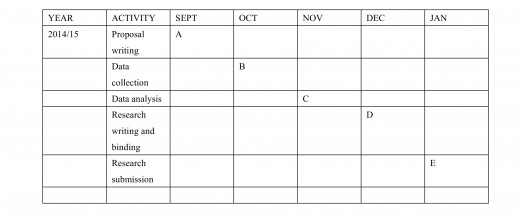
3.8.0 Work plan
A candidate is expected to give a plan/ timetable of his/ her study. This is important in guiding the whole exercise of research.
Example of work plan
References
This should consists of list of books, journals, conference papers, etc cited in the proposal
- This should appear in an independent page
- You should use a common format throughout your work
- Books should be arranged from A-Z
Appendices
- This should also be in a fresh page
- This section should consist of questionnaires/interview guide that you will use in the field. Each category of respondents should have its own list of questions/interview guide.
- Design specific questions for each objective
- Questions set should be in a position to answer your research questions
- Questions should be few in number for them to be effective
- Poor framing of questions will result to poor data
For example:
APPENDIX A: questionnaire/interview guide for Head of school
- This should consist of questions to e answered by Head of schools
- They should be in an independent page
APPENDIX B: questionnaire/interview guide for teachers
- This should consist of questions to be answered by teachers
- They should e in a separate page
APPENDIX C: questionnaire / interview guide for students
- This should consists of questions to be answered by students
- They should e in a separate page.
Physical structure of the proposal
Body text
- Type face – Times New Roman
- Font – 12
- Double spacing
Titles/sub titles
- Body text – full justification
- Titles/subtitles – Bold, centered
Pagination
Pagination shall be at the bottom, center